Volume 12, Issue 3 (Summer 2024)
PCP 2024, 12(3): 275-284 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Farahmand M A, Adibsereshki N, Poshtmashhadi M, Bidhendi R. Influence of Group Active Play on Social Skill and Emotion Regulation in Children With Hearing Impairment. PCP 2024; 12 (3) :275-284
URL: http://jpcp.uswr.ac.ir/article-1-936-en.html
URL: http://jpcp.uswr.ac.ir/article-1-936-en.html
1- Department of Psychology of Exceptional Children, School of Behavioral Sciences and Mental Health, University of Social Welfare and Rehabilitation Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
2- Department of Psychology of Exceptional Children, School of Behavioral Sciences and Mental Health, University of Social Welfare and Rehabilitation Sciences, Tehran, Iran. ,na.adib@hotmail.com
3- Department of Biostatistics and Epidemiology, School of Social Health, University of Social Welfare and Rehabilitation Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
2- Department of Psychology of Exceptional Children, School of Behavioral Sciences and Mental Health, University of Social Welfare and Rehabilitation Sciences, Tehran, Iran. ,
3- Department of Biostatistics and Epidemiology, School of Social Health, University of Social Welfare and Rehabilitation Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
Full-Text [PDF 585 kb]
(1256 Downloads)
| Abstract (HTML) (2253 Views)
Full-Text: (1038 Views)
Introduction
Children with hearing impairments may experience social and behavioral problems. Around 50% of deaf individuals are exposed to educational and rehabilitation programs. Hearing impairment is a crucial factor in the emergence of a wide range of psychiatric disorders, such as anxiety, depression, and some other mental disorders (Nian et al., 2024). The negative impact of this disorder can complicate an individual’s performance (Baradaran & Abdollahzadeh Rafi, 2021; Jiang et al., 2020). It also affects the emotional and social skill (SS) of these children and causes more difficulties in their relationships. Children with hearing impairment demonstrate lower levels of social participation. Reduced hearing ability is one of the factors for reduced social participation in children (Aggarwal et al., 2024). Improving SS in this population can lead to the alleviation of psychological problems, stress, and aggression, ultimately contributing to the overall mental well-being of individuals with hearing impairment (Nurani & Pratiwi, 2020).
Today’s mechanized life has limited children’s vibrant activities, which are considered essential elements of their lives (Al Shloul et al., 2024). The development of many human abilities begins in childhood, and the role of play can be vital in this process. Play is the first motor behavior that children eagerly engage in (Badrotaleyi, 2014). It is a tool through which children learn how to interact with the external world and acquire skills in engaging with others. The role and impact of learning through play were investigated. The pedagogies that align closely with learning through play are those that arise from learning theories, such as active learning, discovery learn-ing, collaborative and cooperative learning, experiential learning, problem-based learning, and Montessori education (Parker & Thomsen, 2019). Play helps children become human, and it is not just childish entertainment (Al Shloul et al., 2024).
The benefits of play are significant and extend beyond the physical health advantages. Play has been widely recognized as an essential part of human development and has been acknowledged by the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights as a fundamental right of every child (Akay, 2023). Although there is no consensus among scholars regarding a comprehensive definition of “play”, common features of playful behaviors include voluntary choice, personal agency, intrinsic motivation, self-directedness, and enjoyment (Nurani & Pratiwi, 2020). Piaget (Piaget, 1983) believed that play may be of crucial importance in children’s cognitive development. His theories about learning focused on children’s needs to explore and experiment for themselves. For Vygotsky (Vygotsky, 1987), play was not only critical for an individual’s cognitive development but also for the social and cultural aspects. Active play involves activities that significantly exceed the level of bodily maintenance during rest. Active play occurs sporadically and with frequent rest periods. However, recent research has shown that active play is associated with moderate to vigorous physical activity (Cheng & Bololia, 2023).
Scientific studies in this field have referred to the relationship between cognitive-motor development and the social development of individuals (Lavega et al., 2014). SS is a set of purposeful behaviors that are context-dependent and under individual control (Darling et al., 2020). Acquiring SS is one of the fundamental elements of socialization for humans in all cultures (Cheng & Bololia, 2023).
Group plays strengthen the collective spirit of children and teach them the necessary skills for social interactions (Mukela, 2020). In group plays, it is necessary for goals to be clear and roles to be coordinated. Play is associated with ER and behavior. Play therapy is a type of therapeutic intervention in which plays are used as a central tool for treating problems and disorders of childhood. Studies on older children have shown that improving mood and emotion is associated with physical and bodily activities (Lavega et al., 2014). Active play can improve many aspects of emotional well-being, such as reducing anxiety, depression, aggression, and sleep problems. Additionally, in adults, physical activity can reduce symptoms of depression and improve cognitive and emotional skills (Zheng et al., 2021). In group plays, children learn cooperation and empathy towards their peers, as well as developing decision-making and problem-solving skills. They realize that winning in a play is not the vital aspect and that fair play and sportsmanship are essential during play interactions (Soto et al., 2024). Group plays can also be beneficial in creating meaningful connections and penetrating the emotional world of children. The utilization of group plays for the growth of deaf and hard-of-hearing children is employed in various areas, such as speech, thinking, learning, academic, emotional, social, and addressing their major issues (Stefanica et al., 2024).
The importance of physical activity and exercise, as well as improving physical health and enhancing emotional well-being, cannot be overstated. It plays a significant role in boosting self-esteem, increasing self-confidence, improving cognitive and emotional skills, and reducing social problems, behavioral issues, academic difficulties, social withdrawal, and social exclusion (Jiang et al., 2020). When interacting with others, our emotions are constantly shaped and influenced by our interpersonal experiences. Most of the time, regulating emotions and emotional behaviors is essential for healthy social relationships (Mulyana et al., 2024).
Active and group plays provide opportunities for communication and promote the development of SS (such as cooperation, problem-solving, and empathy) in individuals, both with and without hearing impairments (Orel & Calik, 2024). When interacting with others, our emo-tions are constantly forming, and interpersonal experi-ences shape us. Even though the importance of active playing is known to many people, children prefer play-ing computer games and they may not know about the negative mental and physical outcomes of those plays. Parents, schools, and professionals should consider and plan for active plays in children’s daily activities. Hear-ing impairment affects a person’s communication, be-havior, and motor development, and limited physical activity, affects the health condition and psychological state of an individual. Even though some studies (Tzanetakos et al., 2017) investigated the effect of some computer games in which children with hearing impairment should do physical activities, most looked at the impact of active play on developing emotional skills and emotional intelligence in children without disabilities and less on children with some kinds of disorder. Also, many studies are not conducted about effect of traditional group active plays (GAP), especially on children with disability. Therefore, this study attempted to investigate; can group active play be effective in the improvement of SS and emotional regulation in children with hearing impairment?
Materials and Methods
The present study was a quasi-experimental pre-test, post-test design with a control group and an 8-week follow-up. The statistical population included all male students with hearing impairments (deaf) aged 7-12 who were studying in schools for students with deafness and hard of hearing (in Karaj City, Iran). Two schools were selected. To detect the optimum sample size, considering a confidence level of 80%, a margin of error of 5%, and referring to the study (Rajabian Dehzireh et al., 2019), the sample size was calculated to be 11 and by inspecting participants’ drops, 30 students were entered in the study. They were randomly placed in experimental and control groups (15 students in each group). The inclusion criteria included boy students with hearing impairments (deaf), not having any mental or physical disorders (observable and stated in their documents), and having parental consent. The exclusion criteria included having more than three consecutive absences and not being willing to continue the sessions in which no one was excluded from the study.
Study measures
SS rating system (SSRS)
The SS rating system (Garsham & Elliot, 1990) is an assessment of students’ social behavior. Based on the rater’s perception of the frequency of the behavior, each item in the scale is rated on a 3-point frequency scale (0=never, 1=sometimes, and 2=very often). The Cronbach’s α coefficient was reported to be0.94. Shahim recorded the Cronbach’s α coefficient of 0.86 for Garsham and Elliot scale in students with hearing impairment.
Emotion regulation (ER) checklist
ER checklist (Shields & Cicchetti, 1997) includes 24 items describing behaviors, the frequency of which is evaluated on a four-point Likert scale (1=never to 4=almost always). The items are distributed in two scales: ER and emotional liability/negativity. The Cronbach’s α coefficient was reported to be 0.76 and 0.69 for negativity/liability and ER (Shafietabar et al., 2020).
Procedure
To implement this research, after receiving the ethical from the university, and coordinating with the Department of Exceptional Education, two boys’ schools for children with deafness were introduced. One of the schools was randomly selected for the experimental group (15 individuals divided randomly into two or three teams according to the type of play) and another one for the control group. In a session, the importance and position of this research were explained to the parents of students, and the intervention plans and goals were explained to them. Also, it was mentioned that they could choose their children to participate or not and were not forced to join. With their approval, the written consent form was obtained from the parents. With the help of school’s counselor, they were given the Griffiths and Elliott SS questionnaires, as well as the Shields and Cicchetti ER parent forms to complete (pre-test). They were instructed on how to answer the questionnaires. For the intervention, in the first stage, necessary explanations regarding the implementation of the plays were given to the students through lip-reading and sign language methods. Also, initial training was provided to enhance security aspects. Then, with the consent of the physical education teacher and the school principal, GAP was implemented during the physical education period for the experimental group two times a week for an hour, while the control group received no intervention. The researcher who was a special teacher instructed and supervised the plays as a facilitator. The group plays used by Ilchizadeh et al. (2021), Foroozanfar, (2014) and those in the book of traditional plays for children and adolescents (Badrotaleyi, 2014) were considered for the intervention. They were revealed by hearing-impaired teachers and university professors and some of them were selected to apply. The aims, descriptions of plays, practices, and activities of intervention sessions are addressed in the Appendix 1.
After the intervention, with the help of schools counselor the parents of both the experimental and control groups completed the Griffiths and Elliott sensation seeking scale (SSS) questionnaires and the Shields and Cicchetti ER as a post-test. Additionally, two months after the post-test, both questionnaires were completed as follow-up by the parents of the participants.
Data analysis
The present study used SPSS software, version 24 for data analysis. Also, descriptive statistics (Mean±SD) and inferential statistics, including covariance test, were used.
Results
Table 1 presents the demographic characteristics of participants. The number of students in the experimental group for 11-12 years old was highest with 7 students and the control group for 9-11 with 7 students.
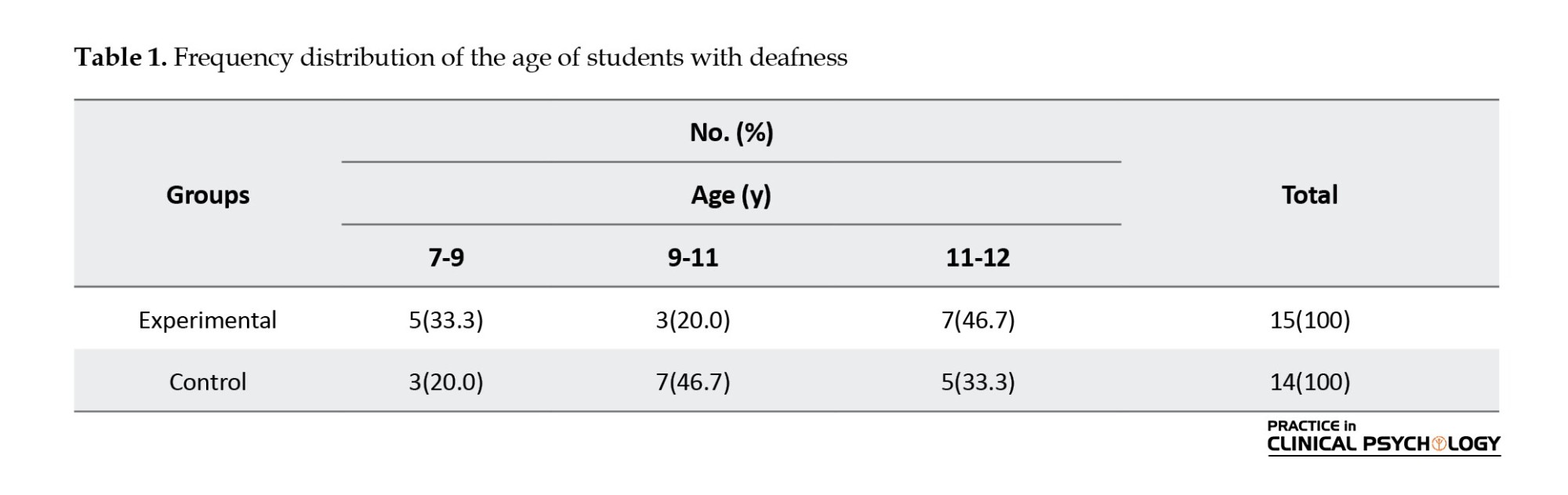
In Table 2, the results showed that the mean of the SS in the pre-test was 43.73 for the experimental group, and it increased to 48.06 in the post-test and 46.93 for the follow-up. The mean score of emotional regulation in the pre-test for the experimental group was 43.33, and it increased to 48.73 in the post-test and 47.53 in the follow-up. However, no significant change was observed in the emotional regulation scores in the post-test and follow-up assessments of the control group.
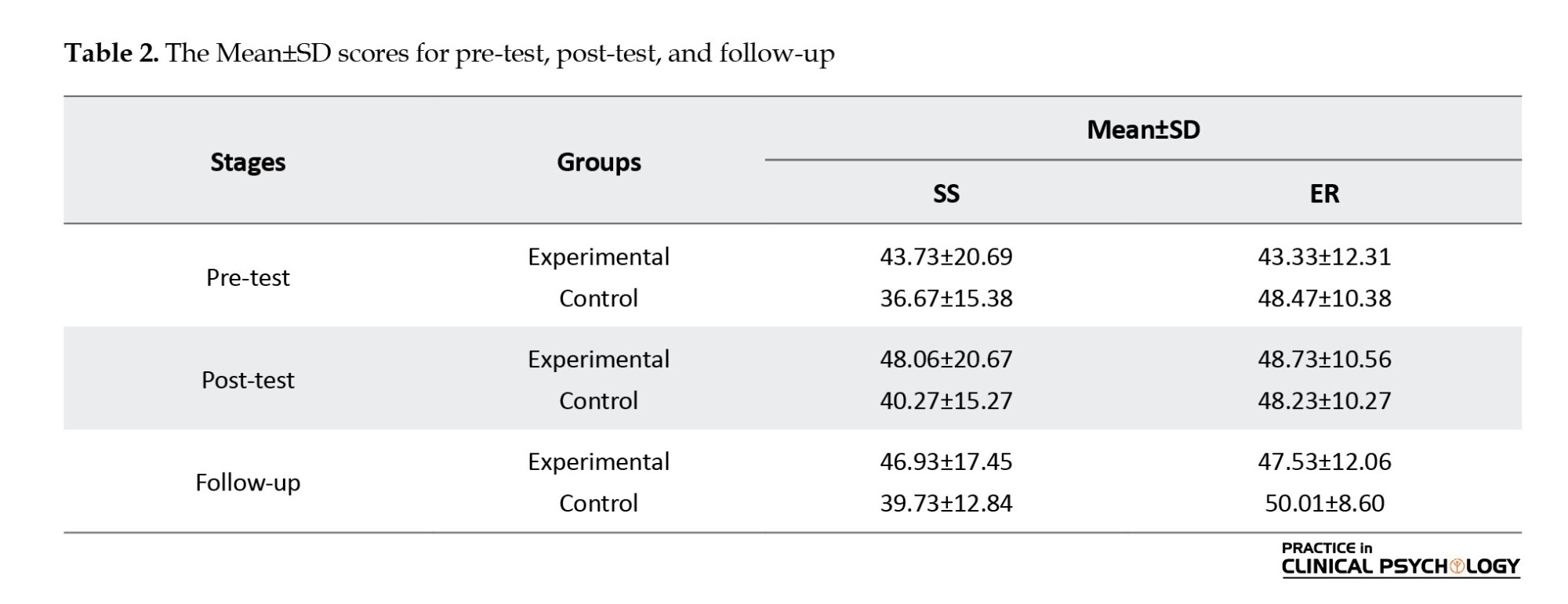
In Table 3, the results indicated that the significance values for both variables are smaller than the significance level of 0.05, indicating that the reported difference in the hypothesis is significant. Additionally, the squared eta (effect size) indicated the influence of time and group variables on the improvement of SS in hearing-impaired students, with the effect size for the combined time and group variable being 0.120, indicating that 12% of the changes in the variable of social relationships are due to the simultaneous effect of these variables. Furthermore, the effect size for the combined time and group variable for emotional regulation is 0.193, indicating that 19.3% of the changes in the emotional regulation variable are due to the simultaneous effect of this variable. In the variable of liability/negativity, the significance values of period and group are 0.022, which are smaller than the significance level of 0.05, indicating that the reported difference in the hypothesis is significant, and active plays have had an impact on the mean liability/negativity. The squared eta (effect size) indicates the influence of time and group variables on the liability/negativity variable. The effect size for the combined time and group variable shows that 12.7% of the changes in the liability/negativity variable are due to the simultaneous effect of these variables.
Discussion
The results of the present study indicated that group active play had a significant effect on SS of students and also those with hearing impairments which is consistent with the results conducted by Hartanto et al., (2021); Ilchizadeh et al. (2021) and Yazdani-Pour and Yazdkhasty. (2012). Some studies focused on the effectiveness of group play on SS and the impact of indigenous-local plays on aspects of social growth and mental health in students, showing social and mental improvements. Hartanto et al.’s study, with a large sample of elementary school students, investigated the effectiveness of indigenous-local plays on SS development, confirming the effectiveness of indigenous-local plays on SS of students. One of the influential factors in enhancing SS is observational learning, where children improve their behavioral patterns by observing the SS of others and modeling their communication and social abilities (Hartanto et al., 2021). Approximately 90% of children with hearing impairments come from families whose primary communication tool is speech, leading these children to experience isolation and lose early natural verbal communication, negatively affecting their speech and communication skills. As a result, they tend towards visual stimuli and computer plays for communication (Nadertabar et al., 2017). Some studies indicate participation in physical activities is associated with greater social integration, such as building friendships and enhancing social skills in children (Su et al., 2018). The benefits are vital for children and adolescents with disabilities (Shields & Synnot, 2016) and those with hearing impairment (Wenhong et al., 2020). In the present study, the instructor used sign language and lip reading to teach the students the rules and process of playing in the group and guide them through it. Thus, group plays allowed students to observe the group interactions and modeling, leading to the enhancement of children’s SS.
Furthermore, the results of this study in terms of ER were consistent with Yazdani-pour & Yazdkhasti (2012), Hansen Sandseter et al., (2023); and Thompson et al., (2019). Hansen Sandseter et al., (2023) researched risk plays in ER, social functioning, and physical health of children which examined six domains of risky plays and showed promising results in terms of effective regulation, and social and physical health. According to the theory of emotion-focused therapy, two processes of arousal and appraisal, which are processed in the right and left hemispheres of the brain, are influential in emotional experiences. Additionally, a brain region called the amygdala plays a significant role in ER. It processes emotional cues based on facial expressions and assists in regulating emotions in individuals. In the present study, it is likely that children with hearing impairments improved their ER through receiving facial expressions in group plays and the effective role of the amygdala in processing emotional cues based on facial change (Thompson et al., 2019).
Active plays have been shown to have a positive impact on reducing negativity/ liability in students with hearing impairments. These results are consistent with the study conducted by Luchoro-Parrilla et al. (2021) on the effectiveness of traditional sports plays in emotional regulation. They indicated that the emotions of children and adolescents who participate in physical activities have significantly improved compared to those who did not participate in physical activities. The involvement of children and adolescents in physical activities is associated with positive emotions. Currently, four different explanations exist in the field of medicine for the impact of physical activities on the emotions of children and adolescents. One perspective focuses on enjoyment and suggests that children and adolescents who experience a diversion from undesirable stimuli during physical activities have a significant improvement in their emotions during and after the activity (Luchoro-Parrilla et al., 2021). Another perspective emphasizes self-efficacy and suggests that physical activities can be considered challenging activities. Regular physical activities may improve emotions and increase self-confidence. The third perspective focuses on social interactions and refers to the presence of social relationships associated with physical activities. Mutual support among individuals participating in physical activities plays a significant role in influencing positive emotions. Therefore, group plays with the rule of inclusiveness at each stage of the activity help reduce the components of liability negativity in regulating emotions in children (Yazdani-pour & Yazdkhasti, 2012).
Conclusion
The present study supports some positive effects of active play intervention on enhancing SS of students with hearing impairment. Additionally, the GAP had been effective in enhancing adaptive emotion and reducing negativity/liability in these students. The schools can plan for active plays to be in the physical education classes for children.
Usually, every research has limitations. One limitation was that two instruments were used in which parents were completed. Also, the study lacked a trained observers or specific instruments to assess the teachers’ work. Future work can concentrate on other groups of children. Also using different instruments completed by self or teachers and considering other aspects of emotions and SS can contribute to these areas. Assessing teacher or trainer’s work can be addressed in future studies.
Ethical Considerations
Compliance with ethical guidelines
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of University of Social Welfare and Rehabilitation Sciences, Tehran, Iran (Code: IR.USWR.REC.1401.159).
Funding
This study did not receive any grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or non-profit sectors.
Authors' contributions
All authors equally contributed to preparing this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully thank the special education office, schools’ personnel, teachers, and students with hearing impairment who participated in this study.
References
Children with hearing impairments may experience social and behavioral problems. Around 50% of deaf individuals are exposed to educational and rehabilitation programs. Hearing impairment is a crucial factor in the emergence of a wide range of psychiatric disorders, such as anxiety, depression, and some other mental disorders (Nian et al., 2024). The negative impact of this disorder can complicate an individual’s performance (Baradaran & Abdollahzadeh Rafi, 2021; Jiang et al., 2020). It also affects the emotional and social skill (SS) of these children and causes more difficulties in their relationships. Children with hearing impairment demonstrate lower levels of social participation. Reduced hearing ability is one of the factors for reduced social participation in children (Aggarwal et al., 2024). Improving SS in this population can lead to the alleviation of psychological problems, stress, and aggression, ultimately contributing to the overall mental well-being of individuals with hearing impairment (Nurani & Pratiwi, 2020).
Today’s mechanized life has limited children’s vibrant activities, which are considered essential elements of their lives (Al Shloul et al., 2024). The development of many human abilities begins in childhood, and the role of play can be vital in this process. Play is the first motor behavior that children eagerly engage in (Badrotaleyi, 2014). It is a tool through which children learn how to interact with the external world and acquire skills in engaging with others. The role and impact of learning through play were investigated. The pedagogies that align closely with learning through play are those that arise from learning theories, such as active learning, discovery learn-ing, collaborative and cooperative learning, experiential learning, problem-based learning, and Montessori education (Parker & Thomsen, 2019). Play helps children become human, and it is not just childish entertainment (Al Shloul et al., 2024).
The benefits of play are significant and extend beyond the physical health advantages. Play has been widely recognized as an essential part of human development and has been acknowledged by the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights as a fundamental right of every child (Akay, 2023). Although there is no consensus among scholars regarding a comprehensive definition of “play”, common features of playful behaviors include voluntary choice, personal agency, intrinsic motivation, self-directedness, and enjoyment (Nurani & Pratiwi, 2020). Piaget (Piaget, 1983) believed that play may be of crucial importance in children’s cognitive development. His theories about learning focused on children’s needs to explore and experiment for themselves. For Vygotsky (Vygotsky, 1987), play was not only critical for an individual’s cognitive development but also for the social and cultural aspects. Active play involves activities that significantly exceed the level of bodily maintenance during rest. Active play occurs sporadically and with frequent rest periods. However, recent research has shown that active play is associated with moderate to vigorous physical activity (Cheng & Bololia, 2023).
Scientific studies in this field have referred to the relationship between cognitive-motor development and the social development of individuals (Lavega et al., 2014). SS is a set of purposeful behaviors that are context-dependent and under individual control (Darling et al., 2020). Acquiring SS is one of the fundamental elements of socialization for humans in all cultures (Cheng & Bololia, 2023).
Group plays strengthen the collective spirit of children and teach them the necessary skills for social interactions (Mukela, 2020). In group plays, it is necessary for goals to be clear and roles to be coordinated. Play is associated with ER and behavior. Play therapy is a type of therapeutic intervention in which plays are used as a central tool for treating problems and disorders of childhood. Studies on older children have shown that improving mood and emotion is associated with physical and bodily activities (Lavega et al., 2014). Active play can improve many aspects of emotional well-being, such as reducing anxiety, depression, aggression, and sleep problems. Additionally, in adults, physical activity can reduce symptoms of depression and improve cognitive and emotional skills (Zheng et al., 2021). In group plays, children learn cooperation and empathy towards their peers, as well as developing decision-making and problem-solving skills. They realize that winning in a play is not the vital aspect and that fair play and sportsmanship are essential during play interactions (Soto et al., 2024). Group plays can also be beneficial in creating meaningful connections and penetrating the emotional world of children. The utilization of group plays for the growth of deaf and hard-of-hearing children is employed in various areas, such as speech, thinking, learning, academic, emotional, social, and addressing their major issues (Stefanica et al., 2024).
The importance of physical activity and exercise, as well as improving physical health and enhancing emotional well-being, cannot be overstated. It plays a significant role in boosting self-esteem, increasing self-confidence, improving cognitive and emotional skills, and reducing social problems, behavioral issues, academic difficulties, social withdrawal, and social exclusion (Jiang et al., 2020). When interacting with others, our emotions are constantly shaped and influenced by our interpersonal experiences. Most of the time, regulating emotions and emotional behaviors is essential for healthy social relationships (Mulyana et al., 2024).
Active and group plays provide opportunities for communication and promote the development of SS (such as cooperation, problem-solving, and empathy) in individuals, both with and without hearing impairments (Orel & Calik, 2024). When interacting with others, our emo-tions are constantly forming, and interpersonal experi-ences shape us. Even though the importance of active playing is known to many people, children prefer play-ing computer games and they may not know about the negative mental and physical outcomes of those plays. Parents, schools, and professionals should consider and plan for active plays in children’s daily activities. Hear-ing impairment affects a person’s communication, be-havior, and motor development, and limited physical activity, affects the health condition and psychological state of an individual. Even though some studies (Tzanetakos et al., 2017) investigated the effect of some computer games in which children with hearing impairment should do physical activities, most looked at the impact of active play on developing emotional skills and emotional intelligence in children without disabilities and less on children with some kinds of disorder. Also, many studies are not conducted about effect of traditional group active plays (GAP), especially on children with disability. Therefore, this study attempted to investigate; can group active play be effective in the improvement of SS and emotional regulation in children with hearing impairment?
Materials and Methods
The present study was a quasi-experimental pre-test, post-test design with a control group and an 8-week follow-up. The statistical population included all male students with hearing impairments (deaf) aged 7-12 who were studying in schools for students with deafness and hard of hearing (in Karaj City, Iran). Two schools were selected. To detect the optimum sample size, considering a confidence level of 80%, a margin of error of 5%, and referring to the study (Rajabian Dehzireh et al., 2019), the sample size was calculated to be 11 and by inspecting participants’ drops, 30 students were entered in the study. They were randomly placed in experimental and control groups (15 students in each group). The inclusion criteria included boy students with hearing impairments (deaf), not having any mental or physical disorders (observable and stated in their documents), and having parental consent. The exclusion criteria included having more than three consecutive absences and not being willing to continue the sessions in which no one was excluded from the study.
Study measures
SS rating system (SSRS)
The SS rating system (Garsham & Elliot, 1990) is an assessment of students’ social behavior. Based on the rater’s perception of the frequency of the behavior, each item in the scale is rated on a 3-point frequency scale (0=never, 1=sometimes, and 2=very often). The Cronbach’s α coefficient was reported to be0.94. Shahim recorded the Cronbach’s α coefficient of 0.86 for Garsham and Elliot scale in students with hearing impairment.
Emotion regulation (ER) checklist
ER checklist (Shields & Cicchetti, 1997) includes 24 items describing behaviors, the frequency of which is evaluated on a four-point Likert scale (1=never to 4=almost always). The items are distributed in two scales: ER and emotional liability/negativity. The Cronbach’s α coefficient was reported to be 0.76 and 0.69 for negativity/liability and ER (Shafietabar et al., 2020).
Procedure
To implement this research, after receiving the ethical from the university, and coordinating with the Department of Exceptional Education, two boys’ schools for children with deafness were introduced. One of the schools was randomly selected for the experimental group (15 individuals divided randomly into two or three teams according to the type of play) and another one for the control group. In a session, the importance and position of this research were explained to the parents of students, and the intervention plans and goals were explained to them. Also, it was mentioned that they could choose their children to participate or not and were not forced to join. With their approval, the written consent form was obtained from the parents. With the help of school’s counselor, they were given the Griffiths and Elliott SS questionnaires, as well as the Shields and Cicchetti ER parent forms to complete (pre-test). They were instructed on how to answer the questionnaires. For the intervention, in the first stage, necessary explanations regarding the implementation of the plays were given to the students through lip-reading and sign language methods. Also, initial training was provided to enhance security aspects. Then, with the consent of the physical education teacher and the school principal, GAP was implemented during the physical education period for the experimental group two times a week for an hour, while the control group received no intervention. The researcher who was a special teacher instructed and supervised the plays as a facilitator. The group plays used by Ilchizadeh et al. (2021), Foroozanfar, (2014) and those in the book of traditional plays for children and adolescents (Badrotaleyi, 2014) were considered for the intervention. They were revealed by hearing-impaired teachers and university professors and some of them were selected to apply. The aims, descriptions of plays, practices, and activities of intervention sessions are addressed in the Appendix 1.
After the intervention, with the help of schools counselor the parents of both the experimental and control groups completed the Griffiths and Elliott sensation seeking scale (SSS) questionnaires and the Shields and Cicchetti ER as a post-test. Additionally, two months after the post-test, both questionnaires were completed as follow-up by the parents of the participants.
Data analysis
The present study used SPSS software, version 24 for data analysis. Also, descriptive statistics (Mean±SD) and inferential statistics, including covariance test, were used.
Results
Table 1 presents the demographic characteristics of participants. The number of students in the experimental group for 11-12 years old was highest with 7 students and the control group for 9-11 with 7 students.

In Table 2, the results showed that the mean of the SS in the pre-test was 43.73 for the experimental group, and it increased to 48.06 in the post-test and 46.93 for the follow-up. The mean score of emotional regulation in the pre-test for the experimental group was 43.33, and it increased to 48.73 in the post-test and 47.53 in the follow-up. However, no significant change was observed in the emotional regulation scores in the post-test and follow-up assessments of the control group.

In Table 3, the results indicated that the significance values for both variables are smaller than the significance level of 0.05, indicating that the reported difference in the hypothesis is significant. Additionally, the squared eta (effect size) indicated the influence of time and group variables on the improvement of SS in hearing-impaired students, with the effect size for the combined time and group variable being 0.120, indicating that 12% of the changes in the variable of social relationships are due to the simultaneous effect of these variables. Furthermore, the effect size for the combined time and group variable for emotional regulation is 0.193, indicating that 19.3% of the changes in the emotional regulation variable are due to the simultaneous effect of this variable. In the variable of liability/negativity, the significance values of period and group are 0.022, which are smaller than the significance level of 0.05, indicating that the reported difference in the hypothesis is significant, and active plays have had an impact on the mean liability/negativity. The squared eta (effect size) indicates the influence of time and group variables on the liability/negativity variable. The effect size for the combined time and group variable shows that 12.7% of the changes in the liability/negativity variable are due to the simultaneous effect of these variables.

Discussion
The results of the present study indicated that group active play had a significant effect on SS of students and also those with hearing impairments which is consistent with the results conducted by Hartanto et al., (2021); Ilchizadeh et al. (2021) and Yazdani-Pour and Yazdkhasty. (2012). Some studies focused on the effectiveness of group play on SS and the impact of indigenous-local plays on aspects of social growth and mental health in students, showing social and mental improvements. Hartanto et al.’s study, with a large sample of elementary school students, investigated the effectiveness of indigenous-local plays on SS development, confirming the effectiveness of indigenous-local plays on SS of students. One of the influential factors in enhancing SS is observational learning, where children improve their behavioral patterns by observing the SS of others and modeling their communication and social abilities (Hartanto et al., 2021). Approximately 90% of children with hearing impairments come from families whose primary communication tool is speech, leading these children to experience isolation and lose early natural verbal communication, negatively affecting their speech and communication skills. As a result, they tend towards visual stimuli and computer plays for communication (Nadertabar et al., 2017). Some studies indicate participation in physical activities is associated with greater social integration, such as building friendships and enhancing social skills in children (Su et al., 2018). The benefits are vital for children and adolescents with disabilities (Shields & Synnot, 2016) and those with hearing impairment (Wenhong et al., 2020). In the present study, the instructor used sign language and lip reading to teach the students the rules and process of playing in the group and guide them through it. Thus, group plays allowed students to observe the group interactions and modeling, leading to the enhancement of children’s SS.
Furthermore, the results of this study in terms of ER were consistent with Yazdani-pour & Yazdkhasti (2012), Hansen Sandseter et al., (2023); and Thompson et al., (2019). Hansen Sandseter et al., (2023) researched risk plays in ER, social functioning, and physical health of children which examined six domains of risky plays and showed promising results in terms of effective regulation, and social and physical health. According to the theory of emotion-focused therapy, two processes of arousal and appraisal, which are processed in the right and left hemispheres of the brain, are influential in emotional experiences. Additionally, a brain region called the amygdala plays a significant role in ER. It processes emotional cues based on facial expressions and assists in regulating emotions in individuals. In the present study, it is likely that children with hearing impairments improved their ER through receiving facial expressions in group plays and the effective role of the amygdala in processing emotional cues based on facial change (Thompson et al., 2019).
Active plays have been shown to have a positive impact on reducing negativity/ liability in students with hearing impairments. These results are consistent with the study conducted by Luchoro-Parrilla et al. (2021) on the effectiveness of traditional sports plays in emotional regulation. They indicated that the emotions of children and adolescents who participate in physical activities have significantly improved compared to those who did not participate in physical activities. The involvement of children and adolescents in physical activities is associated with positive emotions. Currently, four different explanations exist in the field of medicine for the impact of physical activities on the emotions of children and adolescents. One perspective focuses on enjoyment and suggests that children and adolescents who experience a diversion from undesirable stimuli during physical activities have a significant improvement in their emotions during and after the activity (Luchoro-Parrilla et al., 2021). Another perspective emphasizes self-efficacy and suggests that physical activities can be considered challenging activities. Regular physical activities may improve emotions and increase self-confidence. The third perspective focuses on social interactions and refers to the presence of social relationships associated with physical activities. Mutual support among individuals participating in physical activities plays a significant role in influencing positive emotions. Therefore, group plays with the rule of inclusiveness at each stage of the activity help reduce the components of liability negativity in regulating emotions in children (Yazdani-pour & Yazdkhasti, 2012).
Conclusion
The present study supports some positive effects of active play intervention on enhancing SS of students with hearing impairment. Additionally, the GAP had been effective in enhancing adaptive emotion and reducing negativity/liability in these students. The schools can plan for active plays to be in the physical education classes for children.
Usually, every research has limitations. One limitation was that two instruments were used in which parents were completed. Also, the study lacked a trained observers or specific instruments to assess the teachers’ work. Future work can concentrate on other groups of children. Also using different instruments completed by self or teachers and considering other aspects of emotions and SS can contribute to these areas. Assessing teacher or trainer’s work can be addressed in future studies.
Ethical Considerations
Compliance with ethical guidelines
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of University of Social Welfare and Rehabilitation Sciences, Tehran, Iran (Code: IR.USWR.REC.1401.159).
Funding
This study did not receive any grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or non-profit sectors.
Authors' contributions
All authors equally contributed to preparing this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully thank the special education office, schools’ personnel, teachers, and students with hearing impairment who participated in this study.
References
Aggarwal, K., Ravi, R., & Yerraguntla, K. (2024). Impact of hearing loss on social participation in children: A scoping review. Indian Journal of Otolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery : Official Publication of the Association of Otolaryngologists of India, 76(1), 804–810.[DOI:10.1007/s12070-023-04284-1] [PMID]
Al Shloul, T., Mazhar, T., Iqbal, M., yaseen Ghadi, Y., Malik, F., & Hamam, H. (2024). Role of activity-based learning and ChatGPT on students’ performance in education. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence, 6, 100219. [DOI:10.1016/j.caeai.2024.100219]
Akay, E. (2023). Teachers’ opinions on the attending of the hearing-impaired students in the inclusion environment and the resource room services. Journal of Qualitative Research in Education, 33. [DOI:10.14689/enad.33.882]
Badrotaleyi F. (2014). [Traditional Iranian plays for children and adolescents (Persian)]. Tehran: Center of Thinking Development of Children and Adolescents.
Ariapooran, S., Baradaran, M., & Abdolahzadeh Rafi, M. (2021). [Behavioral problems, anxiety, and depression in deaf children and adolescents of mothers with and without fatigue symptoms in the covid-19 outbreak (Persian)]. Research in Cognitive and Behavioral Sciences, 10(2), 129-144. [DOI:10.22108/CBS.2021.129057.1544]
Cheng, Y., & Bololia, L. (2024). The effects of augmented reality on social skills in children with an Autism diagnosis: A preliminary systematic review. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 54(4), 1317–1331. [DOI:10.1007/s10803-022-05878-4] [PMID]
Darling-Hammond, L., Flook, L., Cook-Harvey, C., Barron, B., & Osher, D. (2020). Implications for educational practice of the science of learning and development. Applied Developmental Science, 24(2), 97-140. [DOI:10.1080/10888691.2018.1537791]
Foroozanfar, F. (2014). The effectiveness of group play on creativity of children. National Conference on Future Studies, Humanities and Development.
Ghasempour, A., Akbari, E., Taghipour, M., Azimi, Z., & Refaghat, E. (2012). Comparison of psychological well-being and coping styles in mothers of deaf and normally-hearing children. Audiology, 21(4), 51-59. [Link]
Hansen Sandseter, E. B., Kleppe, R., & Ottesen Kennair, L. E. (2023). Risky play in children’s emotion regulation, social functioning, and physical health: an evolutionary approach. International Journal of Play, 12(1), 127-139. [DOI:10.1080/21594937.2022.2152531]
Hartanto, D., Kusmaedi, N., Ma’mun, A., & Abduljabar, B. (2021). Integrating social skills in traditional games with physical education interventions. International Journal of Human Movement and Sports Sciences, 9(5), 921-928. [DOI:10.13189/saj.2021.090513]
Jiang, F., Kubwimana, C., Eaton, J., Kuper, H., & Bright, T. (2020). Systematic review The relationship between mental health conditions and hearing loss in low-and middle-income countries. Tropical Medicine & International Health: TM & IH, 25(6), 646–659. [DOI:10.1111/tmi.13393] [PMID]
Ilchizadeh, N., Aghdasi, M. T., Hojjat, S., & Sani, Z. (2021). [Effectiveness of native-local games on social development and mental health subscales in 12-14-year-old female students (Persian)]. Sport Psychology Studies, 10(35), 297-316. [Link]
Lavega, P., Alonso, J. I., Etxebeste, J., Lagardera, F., & March, J. (2014). Relationship between traditional games and the intensity of emotions experienced by participants. Research Quarterly for Exercise and Sport, 85(4), 457-467. [DOI:10.1080/02701367.2014.961048] [PMID]
Luchoro-Parrilla, R., Lavega-Burgués, P., Damian-Silva, S., Prat, Q., Sáez de Ocáriz, U., & Ormo-Ribes, E., et al. (2021). Traditional games as cultural heritage: The case of Canary Islands (Spain) from an ethnomotor perspective. Frontiers in Psychology, 12, 586238. [DOI:10.3389/fpsyg.2021.586238] [PMID]
Mukela, R. M. (2022). Indigenous musical play games as cultural resources for the cognitive development promotion in Zambian children: The case of Western province [PhD dissertation]. Zambia: The University of Zambia. [Link]
Mulyana, F. R., Suherman, A., Mahendra, A., Subarjah, H., & Hidayat, Y. (2024). Enhancing social skills: Reliability and validity of the Indonesian version of SSIS-RS among physical education students. Journal Sport Area, 9(1), 11-19. [DOI:10.25299/sportarea.2024.vol9(1).13492]
Nadertabar, M., Sharifi Daramadi, P., Pezeshk, S., & Farrokhi N. (2017). [The influence of computer games on visual-motor skills in deaf students (Persian)]. MEJDS, 7, 101. [Link]
Nian, Q. Y., Cheng, C. A., Cheng, L. H., Lin, Y. Y., Wang, C. H., & Chien, W. C., et al. (2024). Increased risk of psychiatric disorder in patients with hearing loss: A nationwide population-based cohort study. Journal of Translational Medicine, 22(1), 345. [DOI:10.1186/s12967-024-04992-4] [PMID]
Nurani, Y., & Pratiwi, N. (2020). Curriculum design of early childhood life skill based on Indonesian local culture. Paper presented at: Proceedings of the International Conference on Progressive Education (ICOPE 2019). [DOI:10.2991/assehr.k.200323.145]
Örel, M. Z., & ÇALIK, F. (2024). The relationship between mental training skills and emotion regulation in Westlers. International Journal of Eurasian Education and Culture, 9(25), 66-104. [Link]
Parker, R., Thomsen, B. S., & Berry, A. (2022, February). Learning through play at school–A framework for policy and practice. Frontiers in Education 7, 751801. [DOI:10.3389/feduc.2022.751801]
Piaget J. (1983). “Piaget’s theory. In: P. Mussen (Ed). Handbook of child psychology. Vol. 1. New York: Wiley.
Rajabiyan Dehzireh, M., Dortaj, F., Pourroostaei Ardakani, S., & Esmaeili Gojar, S. (2019). [The effect of the use instructional computer games on cognitive emotion regulation and students’ Mindfulness (Persian)]. Technology of Education Journal (TEJ), 13(3), 521-535. [DOI:10.22061/jte.2018.3561.1896]
Shahim S. (2005). [Norming the scale of social skills grading method for preschool children (Persian)]. Iranian Journal of Psychiatry and Clinical Psychology, 11(2), 176-86. [Link]
Shafietabar, M., Akbari Chermahini, S., & Molaei Yasavoli, M. (2020). [Factorial structure and psychometric properties of the emotion regulation checklist - parent form (Persian)]. Quarterly Journal of Child Mental Health, 7(3), 80-95. [DOI:10.52547/jcmh.7.3.8]
Shields, N., & Synnot, A. (2016). Perceived barriers and facilitators to participation in physical activity for children with disability: A qualitative study. BMC Pediatrics, 16, 9. [DOI:10.1186/s12887-016-0544-7] [PMID]
Shields, A., & Cicchetti, D. (1997). Emotion regulation among school-age children: The development and validation of a new criterion Q-sort scale. Developmental Psychology, 33(6), 906–916.
Soto-García, O. H., Sainz, V., Maldonado, A., & Calmaestra, J. (2024). The TEI program for peer tutoring and the prevention of bullying: Its influence on social skills and empathy among secondary school students. Social Sciences, 13(1), 51. [DOI:10.3390/socsci13010051]
Ștefănica, V., Mihai, I., Cojanu, F., Vișan, P. F., Roșu, D., & Potop, V. (2024). Determining the changes in psychomotor behavior of adolescents with special needs. Revista Romaneasca pentru Educatie Multidimensionala, 16(1), 46-70. [DOI:10.18662/rrem/16.1/811]
Su, J., Wu, Z., & Su,Y.(2018). Physical exercise predicts social competence and general well-being in Chinese children 10 to 15 years old: A preliminary study. Child Indicators Research, 11, 1935-1949. [DOI:10.1007/s12187-017-9523-2]
Thompson, N. M., Uusberg, A., Gross, J. J., & Chakrabarti, B. (2019). Empathy and emotion regulation: An integrative account. Progress in Brain Research, 247, 273-304. [DOI:10.1016/bs.pbr.2019.03.024] [PMID]
Tzanetakos, N., Papastergiou, M., Vernadakis, N., & Antoniou, P. (2017). Utilizing physically interactive videogames for the balance training of adolescents with deafness within a physical education course. Journal of Physical Education and Sport, 17(2), 614-623. [DOI: 10.7752/jpes.2017.02093]
Vygotsky, LS. The collected works of L.S. Vygotsky: Child psychology. (1987). New York: Plenum Press. [Link]
Xu, W., Li, C., & Wang, L. (2020). Physical activity of children and adolescents with hearing impairments: A systematic review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(12), 4575. [DOI:10.3390/ijerph17124575] [PMID]
Zheng, L. R., Oberle, C. M., Hawkes-Robinson, W. A., & Daniau, S. (2021). Serious games as a complementary tool for social skill development in young people: A systematic review of the literature. Simulation & Gaming, 52(6), 686-714. [DOI:10.1177/10468781211031283]
Type of Study: Original Research Article |
Subject:
Psychiatry
Received: 2024/04/20 | Accepted: 2024/05/10 | Published: 2024/07/1
Received: 2024/04/20 | Accepted: 2024/05/10 | Published: 2024/07/1
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |









