Volume 6, Issue 4 (Autumn 2018)
PCP 2018, 6(4): 257-264 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Attari A, Ghanbary Hashemabady B A, Mashhadi A, Kareshki H. Temperament and Prosocial Behavior: The Mediating Role of Prosocial Reasoning, Emotion Regulation, and Emotion Lability. PCP 2018; 6 (4) :257-264
URL: http://jpcp.uswr.ac.ir/article-1-561-en.html
URL: http://jpcp.uswr.ac.ir/article-1-561-en.html
1- Department of Psychology, Faculty of Education Sciences and Psychology, Ferdowsi University of Mashhad, Mashhad, Iran.
2- Department of Psychology, Faculty of Education Sciences and Psychology, Ferdowsi University of Mashhad, Mashhad, Iran. ,ghanbarih@um.ac.ir
2- Department of Psychology, Faculty of Education Sciences and Psychology, Ferdowsi University of Mashhad, Mashhad, Iran. ,
Full-Text [PDF 647 kb]
(2974 Downloads)
| Abstract (HTML) (7157 Views)
Full-Text: (2654 Views)
1. Introduction
Psychosocial benefits of prosocial actions (activities intended to benefit others) have been demonstrated in previous studies (Laible, Carlo, & Roesch, 2004; Eisenberg, Fabes, & Spinard, 2006; Tanaka, Afifi, Wathen, Boyle, & Macmillan, 2015). Prosocial behavior is negatively related to antisocial behavior, substance use, anxiety, depressive symptoms and aggressive behavior (e.g. studies by Caprara et al., 2014; McGinley & Carlo, 2007). Moreover, it has other positive outcomes like academic achievement and good peer relationships (Padilla-walker, Fraser, Black, & Bean, 2014).
Investigating the predictors of prosocial behaviors has been the main interest of many researchers. For instance, Carlo et al. (2013) demonstrated that a higher level moral reasoning is linked with other-oriented prosocial behaviors. The capacity of emotion regulation is also known as closely tied to social behavior (McLaughlin, Hatzenbuehler, Mennin, & Nolen-Hoeksema, 2011; Kumru, Carlo, Mestre, & Samper, 2012).
Studies demonstrated a significant relationship between temperamental characteristics and prosocial behavior (Eisenberg et al., 2006; Nigg, 2006; Spinrad & Stifter, 2006). Effortful control and negative affectivity are 2 main factors in these studies. Eisenberg et al. (2006) showed that higher effortful control can prevent antisocial-aggressive behaviors in children. Taylor, Eisenberg, and Spinrad (2015) reported that higher effortful control is associated with more empathetic behavior in children. Spinrad and Stifter (2006) demonstrated that greater negative emotionality is associated with less prosocial behavior. Furthermore, temperamental characteristics are closely associated with emotion regulation and moral reasoning (Van Beveren et al., 2016; Lotfi, Amini, Fathi, Karami, & Ghiasi, 2014). For instance, higher effortful control ability predicts better emotion regulation (Eisenberg, Hofer, Sulik, & Spinrad, 2014). Higher level of executive functioning (i.e. reflected in effortful control) is linked with using more advanced levels of moral reasoning (Hinnant, Nelson, O’Brien, Keane, & Calkins, 2013).
Barger and Derryberry (2013) found that anger and sadness conjointly decrease moral reasoning scores in various dilemmatic stories. Hinnant et al. (2013) suggested that lower levels of emotion regulation interact with lower levels of effortful control, leading to lower moral reasoning in childhood. Although some studies have investigated cognitive and emotional trajectories of prosocial behaviors, an integrated model of cognitive and emotional antecedents is missing (Arsenio & Lemerise, 2004; Malti, Gummerum, & Keller, 2008). We investigated the interaction between cognitive (prosocial moral reasoning) and emotional factors (emotion regulation skill and emotion lability), mediating the relation between temperamental characteristics, and prosocial behavior. Moreover, the non-homogeneity of prosocial behaviors is disregarded in exploring the trajectories of prosocial behavior.
One privilege of our study is to apply Carlo and Randal (2002) theoretical framework, in which 6 types of prosocial behaviors are distinguished according to the motivation by which people involve in such behaviors. Our study provides a better understanding of the interaction of temperament, cognitive and emotional abilities and the motivations behind prosocial behavior. This study aimed to present an integrated model that clarifies how adolescents with various temperament are differently motivated for prosocial behavior and how this path is mediated by prosocial moral reasoning, emotion regulation, and emotional lability. Actually, we hypothesize that effortful control and negative affectivity predict altruistic behavior in the public, through different paths mediated by emotion regulation, emotional lability, and prosocial moral reasoning. We also examined whether gender moderated these models, to assess the model fit.
2. Methods
This was a cross-sectional correlational study conducted in October 2017. The study population consisted of adolescents aged between 10 and 15 years, living in Mashhad City, Iran. Our sample consisted of 202 students (Male=41.5%, Mean±SD=12.8±0.09 years). According to Hair, Celsi, Ortinau, & Bush (2013), a path analysis study requires at least 10 sample for each variable or at least 200 participants. The inclusion criteria consisted of being 10-15 years old and providing informed consent for participation in the research. The exclusion criteria comprised returning incomplete or distorted answers.
We employed a multistage random sampling method. In this method, we selected 5 schools from 5 regions in Mashhad. We asked the headmasters for the list of adolescents aged between 10 and 15 years. Fifty students were randomly selected from each school in such a way that 10 were randomly selected form the list of 10-year-old students, 10 from 11-year-old students and so on.). Finally, we had a sample size of 250 students. Study participants were interviewed about prosocial moral reasoning in a private class at their own school, which took about 45 minutes.
In the interview, five stories of prosocial moral reasoning scale was read to them and their reactions as the main character of the story were asked. Student’s answers were recorded to be scored according to prosocial moral reasoning manual. Their parents were invited to the school to complete the questionnaires on temperament, emotion regulation, and prosocial behavior of their children. Of all, 48 questionnaires were excluded in data analysis due to their missing answers.
To protect confidentiality and anonymity, all students and their parents were allocated codes. Moreover, they were informed that they can discontinue study participation at any stage of the study. We applied Early Adolescent Temperament Questionnaire, Revised (EATQ-R), Prosocial Moral Reasoning Objective Measure (PROM), Prosocial Tendencies Measure, Revised (PTM-R) and Emotion Regulation Checklist (ERC).
Data collection tools were: 1. Early Adolescent Temperament Questionnaire, Revised (EATQ-R) which has 62 items measuring the 3 main domains of temperament: surgency, effortful control, and negative affectivity. Two dimensions of temperaments, including negative affectivity and effortful control, were assessed by two subscales of the Early Adolescent Temperament Questionnaire, Revised (EATQ-R: Ellis & Robarth, 2001). This questionnaire negative affectivity (18 items) reflects the intensity and duration of experiencing negative affects such as anger, fear, and frustration, in unpleasant situations. Negative affectivity is the mean score of the 3 dimensions of frustration, depressive mood and aggression. One sample item of frustration is “I get irritated when I have to stop doing something I enjoy”.
Effortful control (18 items) that reflects the capacity of executive function in adolescents, is the mean score of the 3 dimensions of attentional control, inhibitory control, and activation control. One sample item of attentional control includes “It is easy for me to focus on homework.” Psychometric properties of the EATQ-R have been proved in previous studies (Ellis & Rothbart, 2001). They reported its Cronbach’s alpha values between 0.65 and 0.82 for the subscales. Cronbach’s alpha was acceptable for negative affectivity (α=0.75) and effortful control (α=0.79) in our study;
2. Prosocial Moral Reasoning Objective Measure (PROM: Carlo, Eisenberg, & Knight, 1992) which measures the degree to which people use the 5 types of hedonistic, needs-oriented, approval oriented, stereotypical, and internalized prosocial moral reasoning. This instrument consists of 5 stories that present respondent a situation in which he/she can help another person, when needs are in conflict. The respondent must decide whether to help or not and explain his/her reasons through 5 subsequent questions. The answers clarify participant’s dominant type of reasoning. This study used the total score of prosocial moral reasoning that is the sum of weighted scores of 5 subscales. Hedonistic and approval oriented scores were multiplied by 1, need-oriented and stereotypic scores were multiplied by 2 and internalized scores were multiplied by 3 (see Eisenberg and Murphy, 1995). According to Carlo et al. (2013), Cronbach’s alpha for the 25-item overall composite score of PROM was 0.88 in Spanish speaking samples. The overall Cronbach’s alpha was estimated as 0.69 in the present study;
3. Prosocial Tendencies Measure, Revised (PTM-R) which measures altruistic and public prosocial behavior (Carlo, Hausmann, Christiansen, & Randall, 2003). This instrument encompasses 6 types of prosocial behavior: emotional, compliant, dire, anonymous, altruistic, and public. Altruistic (5 items) behavior refers to prosocial behaviors for which the helper expects no benefits, whereas in public prosocial behavior (4 items), one only helps when his/her behaviors are observed. Some example items include: “I think that one of the best things about helping others is that it makes me look good” (altruistic, reversed), “I can help others best when people are watching” (public). Previous studies have reported acceptable Cronbach’s alpha value for altruistic (α=0.63) and public prosocial behaviors (α=0.74) (Mestre, Carlo, Samper, Tur-Porcar, & Mestre, 2015). Internal consistency was also acceptable (α=0.68 for public, and α=0.71 for altruistic) in our study;
4. Emotion Regulation Checklist (ERC) designed by Shields and Cicchetti (1997) is a 24-item questionnaire that measures two dimensions of emotion regulation. It is scored on a 4-point Likert-type scale, designed to be filled by an adult who knows the child well. Emotion regulation skill (8 items) reflects the social appropriateness of the child’s emotions, emotion understanding, adaptive regulation, and empathy. An example item include “How often is your child cheerful?” Emotion lability/negativity subscale (15 items) assesses the child’s mood swings, anger, and intensity of emotions. e.g. “How quickly does your child’s mood change or how often do they experience mood swings?” Shields and Cicchetti (1997) reported high Cronbach’s alpha values for both emotion regulation (α=0.83) and emotional lability (α=0.96). The Cronbach’s alpha for emotion regulation and emotional lability were 0.78 and 0.81, respectively.
3. Results
Table 1 presents the correlation between the variables in the model. There was a negative association between effortful control and negative affectivity. The adolescents, who experienced more negative affect, had more deficiencies in emotion regulation skills, showed more negative emotional lability, and employed a lower level of prosocial moral reasoning.
Our findings demonstrated that participants, who reported a higher level of effortful control, could regulate their emotions more efficiently, expressed more empathy, and had less mood swings. Moreover, they applied a more advanced level of moral reasoning in dilemmatic situations. In addition, a higher level of emotional lability was related to a lower level of prosocial moral reasoning.
Although there was no significant relationship between public behavior and temperamental dimensions, altruistic behavior was negatively related to negative affectivity and positively associated with effortful control. While, there was a negative correlation between prosocial moral reasoning and public prosocial behavior, altruistic behavior correlated positively with emotion regulation skills and negatively with emotional lability. Moreover, there was a negative association between altruistic and public prosocial behavior.
The hypothesized model
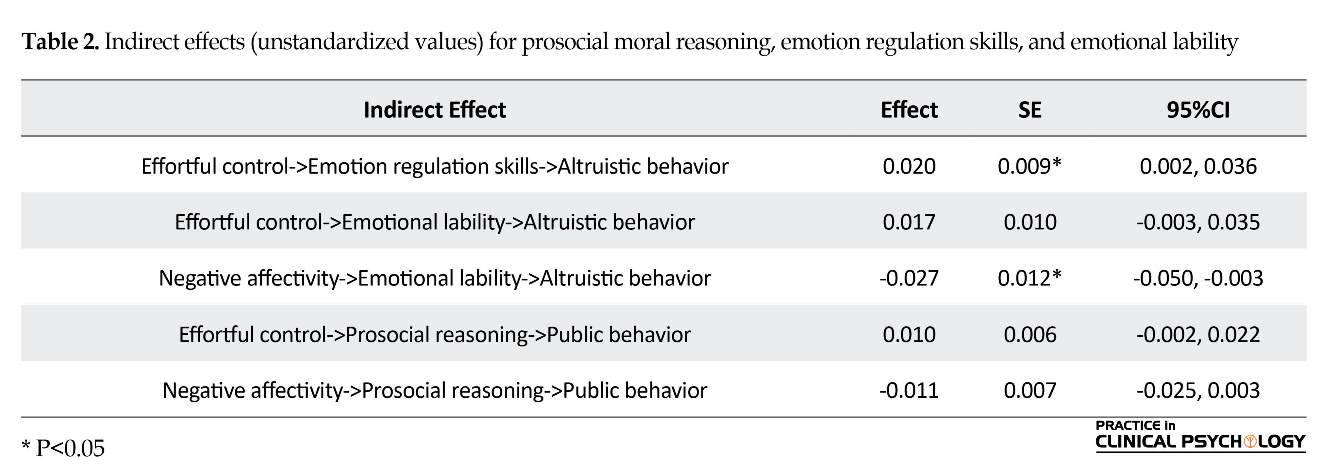
We examined an integrated model of a relation between temperamental dimensions, emotion regulation, moral reasoning, and prosocial behavior, through path analysis modeling with bootstrapping using Mplus 7.4 (Muthen & Muthen, 1988-2012). According to Kline (2005), model fit is good when the Comparative Fit Index (CFI) is greater than 0.95, the Root Mean Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA) is not more than 0.06, and the Standardized Root Mean Square Residual (SRMR) is less than or equal to 0.08. In order to test the significance of the indirect (i.e. mediated) effects, we explored the standard errors, using the delta method (Bollen, 1989).
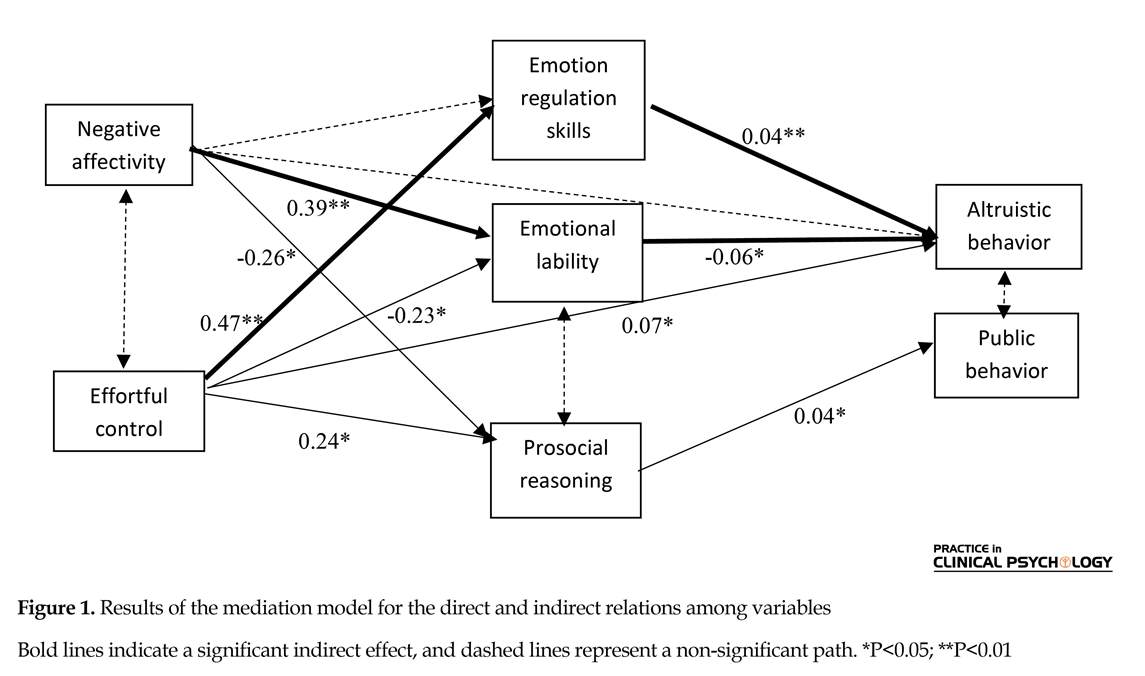
Figure 1 shows the mediation model, in which all significant paths are presented. The model fitted the data well: χ2(8)=12.26, P=0.13, CFI=0.95, RMSEA=0.05, SRMR=0.04. This model indicates that adolescents who
Psychosocial benefits of prosocial actions (activities intended to benefit others) have been demonstrated in previous studies (Laible, Carlo, & Roesch, 2004; Eisenberg, Fabes, & Spinard, 2006; Tanaka, Afifi, Wathen, Boyle, & Macmillan, 2015). Prosocial behavior is negatively related to antisocial behavior, substance use, anxiety, depressive symptoms and aggressive behavior (e.g. studies by Caprara et al., 2014; McGinley & Carlo, 2007). Moreover, it has other positive outcomes like academic achievement and good peer relationships (Padilla-walker, Fraser, Black, & Bean, 2014).
Investigating the predictors of prosocial behaviors has been the main interest of many researchers. For instance, Carlo et al. (2013) demonstrated that a higher level moral reasoning is linked with other-oriented prosocial behaviors. The capacity of emotion regulation is also known as closely tied to social behavior (McLaughlin, Hatzenbuehler, Mennin, & Nolen-Hoeksema, 2011; Kumru, Carlo, Mestre, & Samper, 2012).
Studies demonstrated a significant relationship between temperamental characteristics and prosocial behavior (Eisenberg et al., 2006; Nigg, 2006; Spinrad & Stifter, 2006). Effortful control and negative affectivity are 2 main factors in these studies. Eisenberg et al. (2006) showed that higher effortful control can prevent antisocial-aggressive behaviors in children. Taylor, Eisenberg, and Spinrad (2015) reported that higher effortful control is associated with more empathetic behavior in children. Spinrad and Stifter (2006) demonstrated that greater negative emotionality is associated with less prosocial behavior. Furthermore, temperamental characteristics are closely associated with emotion regulation and moral reasoning (Van Beveren et al., 2016; Lotfi, Amini, Fathi, Karami, & Ghiasi, 2014). For instance, higher effortful control ability predicts better emotion regulation (Eisenberg, Hofer, Sulik, & Spinrad, 2014). Higher level of executive functioning (i.e. reflected in effortful control) is linked with using more advanced levels of moral reasoning (Hinnant, Nelson, O’Brien, Keane, & Calkins, 2013).
Barger and Derryberry (2013) found that anger and sadness conjointly decrease moral reasoning scores in various dilemmatic stories. Hinnant et al. (2013) suggested that lower levels of emotion regulation interact with lower levels of effortful control, leading to lower moral reasoning in childhood. Although some studies have investigated cognitive and emotional trajectories of prosocial behaviors, an integrated model of cognitive and emotional antecedents is missing (Arsenio & Lemerise, 2004; Malti, Gummerum, & Keller, 2008). We investigated the interaction between cognitive (prosocial moral reasoning) and emotional factors (emotion regulation skill and emotion lability), mediating the relation between temperamental characteristics, and prosocial behavior. Moreover, the non-homogeneity of prosocial behaviors is disregarded in exploring the trajectories of prosocial behavior.
One privilege of our study is to apply Carlo and Randal (2002) theoretical framework, in which 6 types of prosocial behaviors are distinguished according to the motivation by which people involve in such behaviors. Our study provides a better understanding of the interaction of temperament, cognitive and emotional abilities and the motivations behind prosocial behavior. This study aimed to present an integrated model that clarifies how adolescents with various temperament are differently motivated for prosocial behavior and how this path is mediated by prosocial moral reasoning, emotion regulation, and emotional lability. Actually, we hypothesize that effortful control and negative affectivity predict altruistic behavior in the public, through different paths mediated by emotion regulation, emotional lability, and prosocial moral reasoning. We also examined whether gender moderated these models, to assess the model fit.
2. Methods
This was a cross-sectional correlational study conducted in October 2017. The study population consisted of adolescents aged between 10 and 15 years, living in Mashhad City, Iran. Our sample consisted of 202 students (Male=41.5%, Mean±SD=12.8±0.09 years). According to Hair, Celsi, Ortinau, & Bush (2013), a path analysis study requires at least 10 sample for each variable or at least 200 participants. The inclusion criteria consisted of being 10-15 years old and providing informed consent for participation in the research. The exclusion criteria comprised returning incomplete or distorted answers.
We employed a multistage random sampling method. In this method, we selected 5 schools from 5 regions in Mashhad. We asked the headmasters for the list of adolescents aged between 10 and 15 years. Fifty students were randomly selected from each school in such a way that 10 were randomly selected form the list of 10-year-old students, 10 from 11-year-old students and so on.). Finally, we had a sample size of 250 students. Study participants were interviewed about prosocial moral reasoning in a private class at their own school, which took about 45 minutes.
In the interview, five stories of prosocial moral reasoning scale was read to them and their reactions as the main character of the story were asked. Student’s answers were recorded to be scored according to prosocial moral reasoning manual. Their parents were invited to the school to complete the questionnaires on temperament, emotion regulation, and prosocial behavior of their children. Of all, 48 questionnaires were excluded in data analysis due to their missing answers.
To protect confidentiality and anonymity, all students and their parents were allocated codes. Moreover, they were informed that they can discontinue study participation at any stage of the study. We applied Early Adolescent Temperament Questionnaire, Revised (EATQ-R), Prosocial Moral Reasoning Objective Measure (PROM), Prosocial Tendencies Measure, Revised (PTM-R) and Emotion Regulation Checklist (ERC).
Data collection tools were: 1. Early Adolescent Temperament Questionnaire, Revised (EATQ-R) which has 62 items measuring the 3 main domains of temperament: surgency, effortful control, and negative affectivity. Two dimensions of temperaments, including negative affectivity and effortful control, were assessed by two subscales of the Early Adolescent Temperament Questionnaire, Revised (EATQ-R: Ellis & Robarth, 2001). This questionnaire negative affectivity (18 items) reflects the intensity and duration of experiencing negative affects such as anger, fear, and frustration, in unpleasant situations. Negative affectivity is the mean score of the 3 dimensions of frustration, depressive mood and aggression. One sample item of frustration is “I get irritated when I have to stop doing something I enjoy”.
Effortful control (18 items) that reflects the capacity of executive function in adolescents, is the mean score of the 3 dimensions of attentional control, inhibitory control, and activation control. One sample item of attentional control includes “It is easy for me to focus on homework.” Psychometric properties of the EATQ-R have been proved in previous studies (Ellis & Rothbart, 2001). They reported its Cronbach’s alpha values between 0.65 and 0.82 for the subscales. Cronbach’s alpha was acceptable for negative affectivity (α=0.75) and effortful control (α=0.79) in our study;
2. Prosocial Moral Reasoning Objective Measure (PROM: Carlo, Eisenberg, & Knight, 1992) which measures the degree to which people use the 5 types of hedonistic, needs-oriented, approval oriented, stereotypical, and internalized prosocial moral reasoning. This instrument consists of 5 stories that present respondent a situation in which he/she can help another person, when needs are in conflict. The respondent must decide whether to help or not and explain his/her reasons through 5 subsequent questions. The answers clarify participant’s dominant type of reasoning. This study used the total score of prosocial moral reasoning that is the sum of weighted scores of 5 subscales. Hedonistic and approval oriented scores were multiplied by 1, need-oriented and stereotypic scores were multiplied by 2 and internalized scores were multiplied by 3 (see Eisenberg and Murphy, 1995). According to Carlo et al. (2013), Cronbach’s alpha for the 25-item overall composite score of PROM was 0.88 in Spanish speaking samples. The overall Cronbach’s alpha was estimated as 0.69 in the present study;
3. Prosocial Tendencies Measure, Revised (PTM-R) which measures altruistic and public prosocial behavior (Carlo, Hausmann, Christiansen, & Randall, 2003). This instrument encompasses 6 types of prosocial behavior: emotional, compliant, dire, anonymous, altruistic, and public. Altruistic (5 items) behavior refers to prosocial behaviors for which the helper expects no benefits, whereas in public prosocial behavior (4 items), one only helps when his/her behaviors are observed. Some example items include: “I think that one of the best things about helping others is that it makes me look good” (altruistic, reversed), “I can help others best when people are watching” (public). Previous studies have reported acceptable Cronbach’s alpha value for altruistic (α=0.63) and public prosocial behaviors (α=0.74) (Mestre, Carlo, Samper, Tur-Porcar, & Mestre, 2015). Internal consistency was also acceptable (α=0.68 for public, and α=0.71 for altruistic) in our study;
4. Emotion Regulation Checklist (ERC) designed by Shields and Cicchetti (1997) is a 24-item questionnaire that measures two dimensions of emotion regulation. It is scored on a 4-point Likert-type scale, designed to be filled by an adult who knows the child well. Emotion regulation skill (8 items) reflects the social appropriateness of the child’s emotions, emotion understanding, adaptive regulation, and empathy. An example item include “How often is your child cheerful?” Emotion lability/negativity subscale (15 items) assesses the child’s mood swings, anger, and intensity of emotions. e.g. “How quickly does your child’s mood change or how often do they experience mood swings?” Shields and Cicchetti (1997) reported high Cronbach’s alpha values for both emotion regulation (α=0.83) and emotional lability (α=0.96). The Cronbach’s alpha for emotion regulation and emotional lability were 0.78 and 0.81, respectively.
3. Results
Table 1 presents the correlation between the variables in the model. There was a negative association between effortful control and negative affectivity. The adolescents, who experienced more negative affect, had more deficiencies in emotion regulation skills, showed more negative emotional lability, and employed a lower level of prosocial moral reasoning.
Our findings demonstrated that participants, who reported a higher level of effortful control, could regulate their emotions more efficiently, expressed more empathy, and had less mood swings. Moreover, they applied a more advanced level of moral reasoning in dilemmatic situations. In addition, a higher level of emotional lability was related to a lower level of prosocial moral reasoning.
Although there was no significant relationship between public behavior and temperamental dimensions, altruistic behavior was negatively related to negative affectivity and positively associated with effortful control. While, there was a negative correlation between prosocial moral reasoning and public prosocial behavior, altruistic behavior correlated positively with emotion regulation skills and negatively with emotional lability. Moreover, there was a negative association between altruistic and public prosocial behavior.
The hypothesized model
We examined an integrated model of a relation between temperamental dimensions, emotion regulation, moral reasoning, and prosocial behavior, through path analysis modeling with bootstrapping using Mplus 7.4 (Muthen & Muthen, 1988-2012). According to Kline (2005), model fit is good when the Comparative Fit Index (CFI) is greater than 0.95, the Root Mean Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA) is not more than 0.06, and the Standardized Root Mean Square Residual (SRMR) is less than or equal to 0.08. In order to test the significance of the indirect (i.e. mediated) effects, we explored the standard errors, using the delta method (Bollen, 1989).
Figure 1 shows the mediation model, in which all significant paths are presented. The model fitted the data well: χ2(8)=12.26, P=0.13, CFI=0.95, RMSEA=0.05, SRMR=0.04. This model indicates that adolescents who
experienced more negative affects behaved less altruistically and this effect was partially mediated by emotional lability (indirect effect, β=-0.02, P=0.02). The adolescents who reported higher degrees of effortful control, illustrated more capacity of behaving altruistically and emotion regulation skills (indirect effect, β=0.02, P=0.03) which mediated this effect. The sum of two indirect effects of emotional lability and emotion regulation on altruistic behavior was significant (β=0.03, P=0.01).There was no significant indirect effect of negative affectivity and effortful control on public behavior (Table 2).
Moderation by gender
We conducted a series of multi-group analysis to examine whether this mediation model is moderated by gender. In this analysis, path coefficients were constrained across the groups in the first model and free to vary, across the groups in the second one. In this analysis, gender is a moderator, if Chi-square, CFI, RMSEA, and SRMR values were significantly different between these nested models. Specifically, moderation exists if the unconstrained model fit indices were significantly better than the constrained model.
Our findings indicated that the constrained model fitted the data well (χ2(9)=13.97, CFI=0.92, RMSEA=0.06, SRMR=0.05) and there is not a significant difference between the Chi-square test results of the constrained model and the unconstrained one ([Δχ2, Δdf=0]=0.38, P>0.05[ns]). Therefore, we concluded that gender did not moderate the model.
4. Discussion
Overall, consistent with previous findings (Laible, Carlo, Murphy, Augustine, & Roesch, 2014), our results show that temperamental factors can predict prosocial behaviors directly and through the mediational role of emotion regulation. However, the direct effect of effortful control, (except for negative affectivity), on altruistic behavior was significant. Our findings demonstrated that the various aspects of temperament are associated with specific types of prosocial behaviors. In addition, individuals with a higher level of negative affectivity, face
Moderation by gender
We conducted a series of multi-group analysis to examine whether this mediation model is moderated by gender. In this analysis, path coefficients were constrained across the groups in the first model and free to vary, across the groups in the second one. In this analysis, gender is a moderator, if Chi-square, CFI, RMSEA, and SRMR values were significantly different between these nested models. Specifically, moderation exists if the unconstrained model fit indices were significantly better than the constrained model.
Our findings indicated that the constrained model fitted the data well (χ2(9)=13.97, CFI=0.92, RMSEA=0.06, SRMR=0.05) and there is not a significant difference between the Chi-square test results of the constrained model and the unconstrained one ([Δχ2, Δdf=0]=0.38, P>0.05[ns]). Therefore, we concluded that gender did not moderate the model.
4. Discussion
Overall, consistent with previous findings (Laible, Carlo, Murphy, Augustine, & Roesch, 2014), our results show that temperamental factors can predict prosocial behaviors directly and through the mediational role of emotion regulation. However, the direct effect of effortful control, (except for negative affectivity), on altruistic behavior was significant. Our findings demonstrated that the various aspects of temperament are associated with specific types of prosocial behaviors. In addition, individuals with a higher level of negative affectivity, face
more difficulties in expressing their emotions and exhibit greater mood swings (emotional lability) which leads to lower degrees of altruistic behavior.
Eisenberg and Fabes (2006) also stated that children with high negative emotionality and low emotion regulation were more prone to externalizing problems and disengaging in prosocial behaviors. Furthermore, effortful control leads to more altruistic behavior, both directly and indirectly. Emotion regulation skill mediates the indirect effect of effortful control on altruistic behavior. This finding is well supported by previous results that showed the predicting role of effortful control and emotion regulation on socio-moral behaviors (Eisenberg, Smith, Sadovsky, & Spinrad, 2004; Eisenberg et al., 2014). This mediation might have some implications for the long lasting debates on the priority of emotions and cognitions, in predicting prosocial behaviors.
Although some paths and mediations were non-significant in our study, they seem noteworthy. For instance, we hypothesized that prosocial moral reasoning mediates the relation between temperament and prosocial behavior. Despite that, data analysis showed no relationship between prosocial moral reasoning and altruistic behavior. This result questions previous findings indicating that higher level of moral reasoning is linked with other-oriented prosocial behaviors (Carlo et al., 2013; Carlo, Koller, Eisenberg, Da Silva, & Frohlich, 1996). This contradiction could be justified by the differences of underlying mechanisms and correlations of prosocial behavior in various cultures (Schwartz, Zamboanga, & Jarvis, 2007; French, Eisenberg, Vaughan, Purwono, & Suryanti, 2008).
Overall, our study showed a relatively stronger role of emotion regulation and emotional lability, than prosocial moral reasoning in predicting prosocial behavior. We presume that the relative importance of cognitive and emotive factors in explaining prosocial behavior may differ in various cultures. This could be a topic for future research. These kind of research studies facilitate developing culture-specific programs for improving prosocial behaviors. Our study presents a model for prosocial behavior which integrates emotional and cognitive variables. Presenting such kind of model can help us design a more detailed interventional plan, according to children’s temperamental profile, as well as cognitive and emotional abilities.
One limitation to our study is disregarding causality, because it lacks a longitudinal design. Future experimental or longitudinal mediation models are needed to provide better evidence for causality. Another limitation is that we applied only self-report instruments and structured interviews which bring about the concern of self-presentation bias and reporter biases. Perhaps multimethod studies (the application of physiological observation methods) are required to replicate our findings and address this gap.
Despite these limitations, our study adds to the literature as it suggests a model explaining how the transaction of temperament, emotive and cognitive factors, predict specific types of prosocial behavior in non-Western populations. This knowledge provides the chance of developing culture and temperament based programs, for improving prosocial behaviors in Iranian adolescents.
Ethical Considerations
Compliance with ethical guidelines
All ethical principles were considered in this article. The participants were informed about the purpose of the research and its implementation stages; They were also assured about the confidentiality of their information; Moreover, They were allowed to leave the study whenever they wish, and if desired, the results of the research would be available to them.
Funding
The present research is a part of first author's PhD thesis in Department of Psychology, Faculty of Education Sciences and Psychology, Ferdowsi University of Mashhad, Iran.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank professor Gustavo Carlo for his precious comments on our paper.
References
Eisenberg and Fabes (2006) also stated that children with high negative emotionality and low emotion regulation were more prone to externalizing problems and disengaging in prosocial behaviors. Furthermore, effortful control leads to more altruistic behavior, both directly and indirectly. Emotion regulation skill mediates the indirect effect of effortful control on altruistic behavior. This finding is well supported by previous results that showed the predicting role of effortful control and emotion regulation on socio-moral behaviors (Eisenberg, Smith, Sadovsky, & Spinrad, 2004; Eisenberg et al., 2014). This mediation might have some implications for the long lasting debates on the priority of emotions and cognitions, in predicting prosocial behaviors.
Although some paths and mediations were non-significant in our study, they seem noteworthy. For instance, we hypothesized that prosocial moral reasoning mediates the relation between temperament and prosocial behavior. Despite that, data analysis showed no relationship between prosocial moral reasoning and altruistic behavior. This result questions previous findings indicating that higher level of moral reasoning is linked with other-oriented prosocial behaviors (Carlo et al., 2013; Carlo, Koller, Eisenberg, Da Silva, & Frohlich, 1996). This contradiction could be justified by the differences of underlying mechanisms and correlations of prosocial behavior in various cultures (Schwartz, Zamboanga, & Jarvis, 2007; French, Eisenberg, Vaughan, Purwono, & Suryanti, 2008).
Overall, our study showed a relatively stronger role of emotion regulation and emotional lability, than prosocial moral reasoning in predicting prosocial behavior. We presume that the relative importance of cognitive and emotive factors in explaining prosocial behavior may differ in various cultures. This could be a topic for future research. These kind of research studies facilitate developing culture-specific programs for improving prosocial behaviors. Our study presents a model for prosocial behavior which integrates emotional and cognitive variables. Presenting such kind of model can help us design a more detailed interventional plan, according to children’s temperamental profile, as well as cognitive and emotional abilities.
One limitation to our study is disregarding causality, because it lacks a longitudinal design. Future experimental or longitudinal mediation models are needed to provide better evidence for causality. Another limitation is that we applied only self-report instruments and structured interviews which bring about the concern of self-presentation bias and reporter biases. Perhaps multimethod studies (the application of physiological observation methods) are required to replicate our findings and address this gap.
Despite these limitations, our study adds to the literature as it suggests a model explaining how the transaction of temperament, emotive and cognitive factors, predict specific types of prosocial behavior in non-Western populations. This knowledge provides the chance of developing culture and temperament based programs, for improving prosocial behaviors in Iranian adolescents.
Ethical Considerations
Compliance with ethical guidelines
All ethical principles were considered in this article. The participants were informed about the purpose of the research and its implementation stages; They were also assured about the confidentiality of their information; Moreover, They were allowed to leave the study whenever they wish, and if desired, the results of the research would be available to them.
Funding
The present research is a part of first author's PhD thesis in Department of Psychology, Faculty of Education Sciences and Psychology, Ferdowsi University of Mashhad, Iran.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank professor Gustavo Carlo for his precious comments on our paper.
References
- Arsenio, W. F., & Lemerise, E. A. (2004). Aggression and moral development: Integrating social information processing and moral domain models. Child Development, 75(4), 987-1002. [DOI:10.1111/j.1467-8624.2004.00720.x] [PMID]
- Barger, B., & Derryberry, W. P. (2013). Do negative mood states impact moral reasoning. Journal of Moral Education, 42(4), 443-59. [DOI:10.1080/03057240.2013.809517]
- Bollen, K. A. (1989). Structural equation modeling with latent variables. New York: John Wiley & Sons. [PMCID]
- Calkins, S. D. (2004). Temperament and emotional regulation: Multiple models of early development. In M. Beauregard (Ed.), Consciousness, Emotional Self-Regulation and The Brain. (pp. 35-59). Amsterdam: John Benjamins Publishing Company. [DOI:10.1075/aicr.54.04cal]
- Caprara, G. V., Luengo Kanacri, B. P., Gerbino, M., Zuffiano, A., Alessandri, G., Vecchio, G. M., et al. (2014). Positive effects of promoting prosocial behavior in early adolescence evidence from a school-based intervention. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 38(4), 386-96. [DOI:10.1177/0165025414531464]
- Carlo, G., Eisenberg, N., & Knight, G. P. (1992). An objective measure of adolescents’ prosocial moral reasoning. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 2(4), 331-49. [DOI:10.1207/s15327795jra0204_3]
- Carlo, G., Hausmann, A., Christiansen, S., & Randall, B. A. (2003). Sociocognitive and behavioral correlates of a measure of prosocial tendencies for adolescents. The Journal of Early Adolescence, 23(1), 107-34. [DOI:10.1177/0272431602239132]
- Carlo, G., Koller, S. H., Eisenberg, N., Da Silva, M., & Frohlich, C. (1996). A cross-national study on the relations among prosocial moral reasoning, gender role orientations, and prosocial behaviors. Developmental Psychology, 32(2), 231-40. [DOI:10.1037/0012-1649.32.2.231]
- Carlo, G., Mestre, M. V., McGinley, M., Tur-Porcar, A., Samper, P., & Streit, C. (2013). The structure and correlates of a measure of prosocial moral reasoning in adolescents from Spain. European Journal of Developmental Psychology, 10(2), 174-89. [DOI:10.1080/17405629.2012.762909]
- Carlo, G., & Randall, B. A. (2002). The development of a measure of prosocial behaviors for late adolescents. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 31(1), 31-44. [DOI:10.1023/A:1014033032440]
- Eisenberg, N., & Fabes, R. (2006). Emotion regulation and children’s socioemotional competence. In L. Balter & C. Tamis-LeMonda (Eds.), Child Psychology: A Handbook of Contemporary Issues (pp. 357–381). New York: Psychology Press.
- Eisenberg, N., Fabes, R. A., Karbon, M., Murphy, B. C., Carlo, G., & Wosinski, M. (1996). Relations of school children’s comforting behavior to empathy-related reactions and shyness. Social Development, 5(3), 330–51. [DOI:10.1111/j.1467-9507.1996.tb00089.x]
- Eisenberg, N., Fabes, R. A., Shepard, S. A., Murphy, B. C., Guthrie, I. K., Jones, S., et al. (1997). Contemporaneous and longitudinal prediction of Children’s social functioning from regulation and emotionality. Child Development, 68(4), 642-64. [DOI:10.2307/1132116] [PMID]
- Eisenberg, N., Fabes, R. A., & Spinrad, T. L. (2006). Prosocial Development. In N. Eisenberg, W. Damon, & R. M. Lerner (Eds.), Handbook of Child Psychology: Social, Emotional, And Personality Development (pp. 646-718). Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons Inc.
- Eisenberg, N., Hofer, C., Sulik, M. J., & Spinrad, T. L. (2014). Self-regulation, effortful control, and their socioemotional correlates. In J. J. Gross (Ed.), Handbook of Emotion Regulation (pp. 157-172). New York: Guilford Press.
- Eisenberg, N., & Murphy, B. (1995). Parenting and children’s moral development. In M. H. Bornstein (Ed.), Handbook of Parenting (vol. 4, pp. 227–57). Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum.
- Eisenberg, N., Smith, C. L., Sadovsky, A., & Spinrad, T. L. (2004). Effortful control: Relations with emotion regulation, adjustment, and socialization in childhood. In R. F. Baumeister & K. D. Vohs (Eds.), Handbook of Self-Regulation: Research, Theory, and Applications (pp. 259-82). New York: Guilford Press.
- Ellis, B., J., & Rothbart, M. (2001). Revision of the Early Adolescent Temperament Questionnaire. Paper Presented at the Society for Research in Child Development Biennial Meeting, Minneapolis, USA, 19-22 April 2001.
- French, D. C., Eisenberg, N., Vaughan, J., Purwono, U., & Suryanti, T. A. (2008). Religious involvement and the social competence and adjustment of Indonesian Muslim adolescents. Developmental Psychology, 44(2), 597-611. [DOI:10.1037/0012-1649.44.2.597] [PMID]
- Hair, J. F, Celsi, M. W., Ortinau, D. J ., & Bush, R. P. (2013) . Essentials of marketing research. New York: McGraw-Hill.
- Hinnant, J. B., Nelson, J. A., O’Brien, M., Keane, S. P., & Calkins, S. D. (2013). the interactive roles of parenting, emotion regulation and executive functioning in moral reasoning during middle childhood. Cognition and Emotion, 27(8), 1460-8. [DOI:10.1080/02699931.2013.789792] [PMID] [PMCID]
- Kline, R. B. (2005). Principles and practice of structural equation modeling. New York: Guilford.
- Kumru, A., Carlo, G., Mestre, V., & Samper, P. (2012). Prosocial moral reasoning and prosocial behavior among Turkish and Spanish adolescents. Social Behavior and Personality, 40(2), 205-14. [DOI:10.2224/sbp.2012.40.2.205]
- Laible, D., Carlo G., Murphy T., Augustine M., & Roesch S. (2014). Predicting Children’s Prosocial and Co-operative Behavior from Their Temperamental Profiles: A Person-centered Approach. Social Development, 23(4), 734-52. [DOI:10.1111/sode.12072]
- Laible, D. J., Carlo, G., & Roesch, S. C. (2004). Pathwaysto self-esteem in late adolescence: The role of parentand peer attachment, empathy, and social behaviors. Journal of Adolescence, 27(6), 703-16. [DOI:10.1016/j.adolescence.2004.05.005] [PMID]
- Lotfi, M., Amini. M., Fathi. A., Karami, A., & Ghiasi, S. (2014). Personality traits, emotion regulation and impulsive behaviors in patients with borderline personality disorder. Journal of Practice Clinical Psychology, 2(1), 27-33.
- Malti, T., Gummerum, M., & Keller, M. (2008). Moral emotions and moral cognitions. European Journal of Developmental Science, 2(3), 203–5.
- McGinley, M. & Carlo, G. (2007). Two sides of the same coin? The relations between prosocial and physically aggressive behaviors. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 36, 337-49. [DOI:10.1007/s10964-006-9095-9] [PMID]
- McLaughlin, K. A., Hatzenbuehler, M. L., Mennin, D. S., & Nolen-Hoeksema, S. (2011). Emotion dysregulation and adolescent psychopathology: A prospective study. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 49(9), 544-54. [DOI:10.1016/j.brat.2011.06.003] [PMID] [PMCID]
- Mestre, M. V., Carlo, G., Samper, P., Tur-Purcar, A. M., & Mestre, A. L (2015). Psychometric Evidence of a Multidimensional Measure of Prosocial Behaviors for Spanish Adolescents. The Journal of Genetic Psychology, 176(4), 260-71.
- Muthen, L. K., & Muthen, B. O. (1998-2012). Mplususer’s guide. Los Angeles: Muthén & Muthén.
- Nigg, J. T. (2006). Temperament and developmental psychopathology. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 47(3-4), 395-422. [DOI:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2006.01612.x] [PMID]
- Padilla-walker, L. M., Fraser, A. M., Black, B. B., & Bean, R. A. (2014). Associations between friendship, sympathy, and prosocial behavior toward friends. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 25(1), 28-35. [DOI:10.1111/jora.12108]
- Schwartz, S. J., Zamboanga, B. L., & Jarvis, L. (2007). Ethnic identity and acculturation in Hispanic early adolescents: Mediated relationships to academic grades, prosocial behaviors, and externalizing symptoms. Cultural Diversity and Ethnic Minority Psychology, 13(4), 364-73. [DOI:10.1037/1099-9809.13.4.364] [PMID]
- Shields, A., & Cicchetti, D. (1997). Emotion regulation among school-age children: The development and validation of a new criterion Q-sort scale. Developmental Psychology, 33(6), 906-16. [DOI:10.1037/0012-1649.33.6.906] [PMID]
- Spinrad, T. L. & Stifter, C. A. (2006). Toddlers’ empathy-related responding to distress: Predictions from negative emotionality and maternal behavior in infancy. Infancy, 10(2), 97-121. [DOI:10.1207/s15327078in1002_1]
- Tanaka, M., Afifi, T. O., Wathen, C. N., & Boyle, M. H., Macmillan, H. L. (2015). Evaluation of sex differences inhealth-related quality of life outcomesassociated with child abuse: Results from the Ontario Child Health Study. Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences, 24(4):353-63. [DOI:10.1017/S2045796014000274] [PMID]
- Taylor, Z. E., Eisenberg, N., & Spinrad, T. L. (2015). Respiratory sinus arrhythmia, effortful control, and parenting as predictors of children’s sympathy across early childhood. Developmental Psychology, 51(1), 17-25. [DOI:10.1037/a0038189] [PMID] [PMCID]
- Van Beveren, M. L., McIntosh, K., Vandevivere, E., Wante, L., Vandeweghe, L., Van Durme, K et al. (2016). Associations between temperament, emotion regulation, and depression in youth: the role of positive temperament. Journal of Child and Family Studies. 25(6), 1954-68. [DOI:10.1007/s10826-016-0368-y]
Type of Study: Original Research Article |
Subject:
Cognitive behavioral
Received: 2018/01/10 | Accepted: 2018/06/25 | Published: 2018/10/1
Received: 2018/01/10 | Accepted: 2018/06/25 | Published: 2018/10/1
References
1. Arsenio, W. F., & Lemerise, E. A. (2004). Aggression and moral development: Integrating social information processing and moral domain models. Child Development, 75(4), 987-1002. [DOI:10.1111/j.1467-8624.2004.00720.x] [PMID] [DOI:10.1111/j.1467-8624.2004.00720.x]
2. Barger, B., & Derryberry, W. P. (2013). Do negative mood states impact moral reasoning. Journal of Moral Education, 42(4), 443-59. [DOI:10.1080/03057240.2013.809517] [DOI:10.1080/03057240.2013.809517]
3. Bollen, K. A. (1989). Structural equation modeling with latent variables. New York: John Wiley & Sons. [PMCID] [PMCID]
4. Calkins, S. D. (2004). Temperament and emotional regulation: Multiple models of early development. In M. Beauregard (Ed.), Consciousness, Emotional Self-Regulation and The Brain. (pp. 35-59). Amsterdam: John Benjamins Publishing Company. [DOI:10.1075/aicr.54.04cal] [DOI:10.1075/aicr.54.04cal]
5. Caprara, G. V., Luengo Kanacri, B. P., Gerbino, M., Zuffiano, A., Alessandri, G., Vecchio, G. M., et al. (2014). Positive effects of promoting prosocial behavior in early adolescence evidence from a school-based intervention. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 38(4), 386-96. [DOI:10.1177/0165025414531464] [DOI:10.1177/0165025414531464]
6. Carlo, G., Eisenberg, N., & Knight, G. P. (1992). An objective measure of adolescents' prosocial moral reasoning. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 2(4), 331-49. [DOI:10.1207/s15327795jra0204_3] [DOI:10.1207/s15327795jra0204_3]
7. Carlo, G., Hausmann, A., Christiansen, S., & Randall, B. A. (2003). Sociocognitive and behavioral correlates of a measure of prosocial tendencies for adolescents. The Journal of Early Adolescence, 23(1), 107-34. [DOI:10.1177/0272431602239132] [DOI:10.1177/0272431602239132]
8. Carlo, G., Koller, S. H., Eisenberg, N., Da Silva, M., & Frohlich, C. (1996). A cross-national study on the relations among prosocial moral reasoning, gender role orientations, and prosocial behaviors. Developmental Psychology, 32(2), 231-40. [DOI:10.1037/0012-1649.32.2.231] [DOI:10.1037/0012-1649.32.2.231]
9. Carlo, G., Mestre, M. V., McGinley, M., Tur-Porcar, A., Samper, P., & Streit, C. (2013). The structure and correlates of a measure of prosocial moral reasoning in adolescents from Spain. European Journal of Developmental Psychology, 10(2), 174-89. [DOI:10.1080/17405629.2012.762909] [DOI:10.1080/17405629.2012.762909]
10. Carlo, G., & Randall, B. A. (2002). The development of a measure of prosocial behaviors for late adolescents. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 31(1), 31-44. [DOI:10.1023/A:1014033032440] [DOI:10.1023/A:1014033032440]
11. Eisenberg, N., & Fabes, R. (2006). Emotion regulation and children's socioemotional competence. In L. Balter & C. Tamis-LeMonda (Eds.), Child Psychology: A Handbook of Contemporary Issues (pp. 357–381). New York: Psychology Press.
12. Eisenberg, N., Fabes, R. A., Karbon, M., Murphy, B. C., Carlo, G., & Wosinski, M. (1996). Relations of school children's comforting behavior to empathy-related reactions and shyness. Social Development, 5(3), 330–51. [DOI:10.1111/j.1467-9507.1996.tb00089.x] [DOI:10.1111/j.1467-9507.1996.tb00089.x]
13. Eisenberg, N., Fabes, R. A., Shepard, S. A., Murphy, B. C., Guthrie, I. K., Jones, S., et al. (1997). Contemporaneous and longitudinal prediction of Children's social functioning from regulation and emotionality. Child Development, 68(4), 642-64. [DOI:10.2307/1132116] [PMID] [DOI:10.2307/1132116]
14. Eisenberg, N., Fabes, R. A., & Spinrad, T. L. (2006). Prosocial Development. In N. Eisenberg, W. Damon, & R. M. Lerner (Eds.), Handbook of Child Psychology: Social, Emotional, And Personality Development (pp. 646-718). Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons Inc.
15. Eisenberg, N., Hofer, C., Sulik, M. J., & Spinrad, T. L. (2014). Self-regulation, effortful control, and their socioemotional correlates. In J. J. Gross (Ed.), Handbook of Emotion Regulation (pp. 157-172). New York: Guilford Press.
16. Eisenberg, N., & Murphy, B. (1995). Parenting and children's moral development. In M. H. Bornstein (Ed.), Handbook of Parenting (vol. 4, pp. 227–57). Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum.
17. Eisenberg, N., Smith, C. L., Sadovsky, A., & Spinrad, T. L. (2004). Effortful control: Relations with emotion regulation, adjustment, and socialization in childhood. In R. F. Baumeister & K. D. Vohs (Eds.), Handbook of Self-Regulation: Research, Theory, and Applications (pp. 259-82). New York: Guilford Press.
18. Ellis, B., J., & Rothbart, M. (2001). Revision of the Early Adolescent Temperament Questionnaire. Paper Presented at the Society for Research in Child Development Biennial Meeting, Minneapolis, USA, 19-22 April 2001.
19. French, D. C., Eisenberg, N., Vaughan, J., Purwono, U., & Suryanti, T. A. (2008). Religious involvement and the social competence and adjustment of Indonesian Muslim adolescents. Developmental Psychology, 44(2), 597-611. [DOI:10.1037/0012-1649.44.2.597] [PMID] [DOI:10.1037/0012-1649.44.2.597]
20. Hair, J. F, Celsi, M. W., Ortinau, D. J ., & Bush, R. P. (2013) . Essentials of marketing research. New York: McGraw-Hill.
21. Hinnant, J. B., Nelson, J. A., O'Brien, M., Keane, S. P., & Calkins, S. D. (2013). the interactive roles of parenting, emotion regulation and executive functioning in moral reasoning during middle childhood. Cognition and Emotion, 27(8), 1460-8. [DOI:10.1080/02699931.2013.789792] [PMID] [PMCID] [DOI:10.1080/02699931.2013.789792]
22. Kline, R. B. (2005). Principles and practice of structural equation modeling. New York: Guilford.
23. Kumru, A., Carlo, G., Mestre, V., & Samper, P. (2012). Prosocial moral reasoning and prosocial behavior among Turkish and Spanish adolescents. Social Behavior and Personality, 40(2), 205-14. [DOI:10.2224/sbp.2012.40.2.205] [DOI:10.2224/sbp.2012.40.2.205]
24. Laible, D., Carlo G., Murphy T., Augustine M., & Roesch S. (2014). Predicting Children's Prosocial and Co-operative Behavior from Their Temperamental Profiles: A Person-centered Approach. Social Development, 23(4), 734-52. [DOI:10.1111/sode.12072] [DOI:10.1111/sode.12072]
25. Laible, D. J., Carlo, G., & Roesch, S. C. (2004). Pathwaysto self-esteem in late adolescence: The role of parentand peer attachment, empathy, and social behaviors. Journal of Adolescence, 27(6), 703-16. [DOI:10.1016/j.adolescence.2004.05.005] [PMID] [DOI:10.1016/j.adolescence.2004.05.005]
26. Lotfi, M., Amini. M., Fathi. A., Karami, A., & Ghiasi, S. (2014). Personality traits, emotion regulation and impulsive behaviors in patients with borderline personality disorder. Journal of Practice Clinical Psychology, 2(1), 27-33.
27. Malti, T., Gummerum, M., & Keller, M. (2008). Moral emotions and moral cognitions. European Journal of Developmental Science, 2(3), 203–5.
28. McGinley, M. & Carlo, G. (2007). Two sides of the same coin? The relations between prosocial and physically aggressive behaviors. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 36, 337-49. [DOI:10.1007/s10964-006-9095-9] [PMID] [DOI:10.1007/s10964-006-9095-9]
29. McLaughlin, K. A., Hatzenbuehler, M. L., Mennin, D. S., & Nolen-Hoeksema, S. (2011). Emotion dysregulation and adolescent psychopathology: A prospective study. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 49(9), 544-54. [DOI:10.1016/j.brat.2011.06.003] [PMID] [PMCID] [DOI:10.1016/j.brat.2011.06.003]
30. Mestre, M. V., Carlo, G., Samper, P., Tur-Purcar, A. M., & Mestre, A. L (2015). Psychometric Evidence of a Multidimensional Measure of Prosocial Behaviors for Spanish Adolescents. The Journal of Genetic Psychology, 176(4), 260-71. [DOI:10.1080/00221325.2015.1052726] [PMID]
31. Muthen, L. K., & Muthen, B. O. (1998-2012). Mplususer's guide. Los Angeles: Muthén & Muthén.
32. Nigg, J. T. (2006). Temperament and developmental psychopathology. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 47(3-4), 395-422. [DOI:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2006.01612.x] [PMID] [DOI:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2006.01612.x]
33. Padilla-walker, L. M., Fraser, A. M., Black, B. B., & Bean, R. A. (2014). Associations between friendship, sympathy, and prosocial behavior toward friends. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 25(1), 28-35. [DOI:10.1111/jora.12108] [DOI:10.1111/jora.12108]
34. Schwartz, S. J., Zamboanga, B. L., & Jarvis, L. (2007). Ethnic identity and acculturation in Hispanic early adolescents: Mediated relationships to academic grades, prosocial behaviors, and externalizing symptoms. Cultural Diversity and Ethnic Minority Psychology, 13(4), 364-73. [DOI:10.1037/1099-9809.13.4.364] [PMID] [DOI:10.1037/1099-9809.13.4.364]
35. Shields, A., & Cicchetti, D. (1997). Emotion regulation among school-age children: The development and validation of a new criterion Q-sort scale. Developmental Psychology, 33(6), 906-16. [DOI:10.1037/0012-1649.33.6.906] [PMID] [DOI:10.1037/0012-1649.33.6.906]
36. Spinrad, T. L. & Stifter, C. A. (2006). Toddlers' empathy-related responding to distress: Predictions from negative emotionality and maternal behavior in infancy. Infancy, 10(2), 97-121. [DOI:10.1207/s15327078in1002_1] [DOI:10.1207/s15327078in1002_1]
37. Tanaka, M., Afifi, T. O., Wathen, C. N., & Boyle, M. H., Macmillan, H. L. (2015). Evaluation of sex differences inhealth-related quality of life outcomesassociated with child abuse: Results from the Ontario Child Health Study. Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences, 24(4):353-63. [DOI:10.1017/S2045796014000274] [PMID] [DOI:10.1017/S2045796014000274]
38. Taylor, Z. E., Eisenberg, N., & Spinrad, T. L. (2015). Respiratory sinus arrhythmia, effortful control, and parenting as predictors of children's sympathy across early childhood. Developmental Psychology, 51(1), 17-25. [DOI:10.1037/a0038189] [PMID] [PMCID] [DOI:10.1037/a0038189]
39. Van Beveren, M. L., McIntosh, K., Vandevivere, E., Wante, L., Vandeweghe, L., Van Durme, K et al. (2016). Associations between temperament, emotion regulation, and depression in youth: the role of positive temperament. Journal of Child and Family Studies. 25(6), 1954-68. [DOI:10.1007/s10826-016-0368-y] [DOI:10.1007/s10826-016-0368-y]
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |